Table of Contents
![]()
Introduction
Red algae, scientifically classified under the phylum Rhodophyta, are a diverse group of marine organisms with a fascinating array of unique characteristics. They play a significant role in marine ecosystems and have a variety of practical uses in various industries. In this article, we will delve into the taxonomy, distinctive features, and the numerous applications of red algae.
Taxonomy and Classification of Red Algae
Phylum Rhodophyta: Red algae belong to the phylum Rhodophyta, which comprises over 7,000 known species. These species exhibit remarkable diversity in size, shape, and habitat preferences. They are primarily found in marine environments, ranging from tide pools to deep ocean waters. The classification of red algae is based on a combination of genetic, morphological, and physiological characteristics.
Unique Characteristics of Red Algae
- Pigments and Photosynthesis: Red algae are known for their unique pigments, including chlorophyll-a and a distinctive red pigment called phycoerythrin. These pigments allow red algae to photosynthesize efficiently in deeper waters where blue and green light is scarce.
- Cell Wall Composition: Unlike most algae and plants, red algae possess a cell wall primarily composed of cellulose and complex polysaccharides like agar and carrageenan. This unique cell wall structure contributes to their resilience in various environmental conditions.
- Reproduction Strategies: Red algae exhibit diverse reproductive strategies, including sexual and asexual methods. Some species release spores, while others have complex life cycles involving alternation of generations, adding to their biological complexity.
- Adaptations to Marine Environments: Red algae have evolved numerous adaptations to thrive in marine environments, such as their ability to tolerate high levels of salinity and temperature fluctuations.
Uses of Red Algae
Red algae have a wide range of practical applications across different industries:
- Food and Culinary Applications: Red algae are a staple in Asian cuisine, particularly in the production of sushi and nori. Additionally, carrageenan, a substance derived from red algae, is used as a gelling agent and stabilizer in various food products.
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals: Red algae are a valuable source of agar, which is widely used in microbiology laboratories for bacterial culture. Furthermore, they contain compounds with potential medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and antiviral agents.
- Industrial Applications: Alginates extracted from certain red algae are used in textiles, paper production, and the pharmaceutical industry. They have excellent water-holding properties and are used in wound dressings and as thickeners in various products.
- Ecological Importance: Red algae contribute to the formation of coral reefs by providing a substrate for coral larvae to settle on. They also serve as crucial habitat and nursery grounds for various marine organisms.
Red Algae Conservation
While red algae provide numerous benefits, they face threats such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these valuable organisms. Initiatives to establish marine protected areas can help safeguard red algae populations and the ecosystems they support.
Future Directions and Research
The future of red algae research holds promise for discovering new uses and applications. Researchers are also studying how climate change affects red algae populations and their ecological roles. Further taxonomic studies will enhance our understanding of the diversity within the phylum Rhodophyta.
Conclusion
Red algae are remarkable organisms with unique characteristics that make them vital components of marine ecosystems and valuable resources for various industries. Understanding their taxonomy, characteristics, and applications is not only scientifically enriching but also essential for their conservation and sustainable use. As we continue to explore the potential of red algae, it is imperative that we balance our utilization with responsible conservation practices to ensure their long-term survival and contributions to our world.
Share This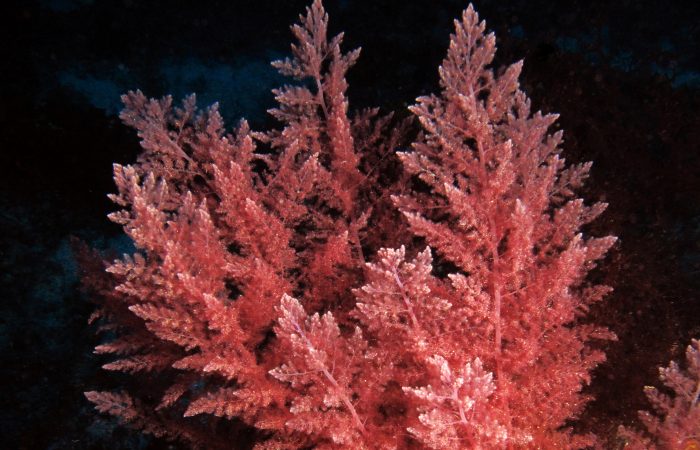




Be the first to comment