Table of Contents
![]()
Social media has become an integral part of modern life, shaping how we connect, share, and interact with others. Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, TikTok, and Snapchat offer unprecedented opportunities for communication and expression. However, as social media’s influence grows, so do concerns about its impact on mental health. This article explores the various effects of social media on mental health, examining both positive and negative aspects, and discusses strategies for mitigating adverse effects.
Positive Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
Social Connection and Support
One of the primary benefits of social media is its ability to connect individuals. Social media platforms facilitate the maintenance of relationships with friends and family, even over long distances. This connectivity is particularly beneficial for those who might otherwise feel isolated. Additionally, social media provides access to various support groups and communities focused on mental health issues. These platforms allow individuals to share experiences, seek advice, and find solace in knowing they are not alone.
Awareness and Education
Social media plays a crucial role in raising awareness about mental health issues. Through posts, articles, and campaigns, users can learn about various conditions, treatment options, and coping strategies. This increased awareness helps reduce stigma and encourages individuals to seek help when needed. Moreover, educational resources and self-help tools are readily available, offering valuable information on managing mental health.
Self-Expression and Creativity
For many, social media serves as a platform for artistic expression and creativity. Users can share their artwork, writing, music, and other forms of creative output with a global audience. This self-expression can be therapeutic and empowering, providing a sense of accomplishment and connection. Social media also offers opportunities for personal growth and development, as individuals explore new interests and engage with diverse communities.
Negative Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
Anxiety and Depression
While social media can foster connection, it can also contribute to anxiety and depression. One significant factor is social comparison. Users often compare themselves to others based on curated posts showcasing idealized versions of life, which can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. Additionally, cyberbullying and online harassment are prevalent issues that can have severe emotional consequences, exacerbating feelings of anxiety and depression.
Addiction and Time Management
Social media addiction is a growing concern, characterized by compulsive use and difficulty managing time. The design of social media platforms, with their endless feeds and notifications, can encourage prolonged use, often at the expense of productivity and real-world interactions. This addiction can disrupt daily routines and negatively impact work, school performance, and personal relationships.
Sleep Disruption
The use of social media, particularly before bedtime, can negatively affect sleep quality. The blue light emitted by screens interferes with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Additionally, engaging with stimulating content or social interactions late at night can delay sleep onset and disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and decreased overall well-being.
Mechanisms Behind Social Media’s Impact on Mental Health
Psychological Theories
Several psychological theories help explain the impact of social media on mental health. Social Comparison Theory suggests that individuals evaluate themselves based on comparisons with others. When users see others’ idealized posts, it can lead to negative self-assessment and diminished self-esteem. Self-Discrepancy Theory posits that discrepancies between one’s actual self and ideal self can cause emotional distress. Social media can exacerbate these discrepancies by presenting an idealized version of reality.
Algorithms and Engagement
Social media platforms use algorithms to tailor content to users’ interests and behaviors. These algorithms prioritize engaging content, which can perpetuate exposure to negative or distressing material. The pursuit of likes, comments, and shares can create a feedback loop that reinforces certain behaviors, potentially leading to increased anxiety and decreased satisfaction.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and Loneliness
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) is a psychological phenomenon where individuals feel anxious about missing out on rewarding experiences that others are having. Social media amplifies FOMO by providing constant updates on others’ activities, which can contribute to feelings of loneliness and isolation. Despite being connected online, users may experience a lack of meaningful interactions in their offline lives.
Populations Most Affected
Adolescents and Young Adults
Adolescents and young adults are particularly vulnerable to the effects of social media. Developmental stages involving identity formation and peer pressure make this group more susceptible to the negative impacts of social comparison and cyberbullying. Social media can significantly influence their self-esteem and mental health during these formative years.
Adults and Older Individuals
Social media also affects adults and older individuals, though in different ways. For professionals, social media can blur boundaries between work and personal life, leading to stress and burnout. For older adults, social media can offer valuable connections and opportunities but can also be a source of stress, particularly if they struggle with new technology or face online harassment.
Vulnerable Groups
Certain groups, including individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions and marginalized communities, may experience heightened negative effects from social media. For those already struggling with mental health issues, social media can exacerbate symptoms or create additional stressors. Marginalized communities might face targeted harassment or exclusion, further impacting their mental health.
Strategies for Mitigating Negative Effects
Personal Strategies
Individuals can adopt several strategies to mitigate the negative effects of social media. Setting boundaries, such as limiting screen time and designating specific times for social media use, can help manage exposure. Curating social media feeds to include positive and uplifting content can also improve overall well-being. Engaging in offline activities and maintaining real-world relationships can provide balance and reduce reliance on social media for social fulfillment.
Professional and Organizational Strategies
Mental health education and resources in the workplace and educational settings can help individuals understand and manage the effects of social media. Organizations can implement policies to promote healthier social media use and create supportive environments for employees and students. Providing access to mental health resources and counseling services can also support those struggling with social media-related issues.
Role of Technology Companies
Technology companies have a role in addressing the impact of social media on mental health. Ethical design practices, such as minimizing addictive features and promoting user well-being, can contribute to healthier social media experiences. Implementing features that allow users to manage their engagement and providing resources for mental health support can also be beneficial.
Future Directions and Research
Emerging Trends in Social Media
The landscape of social media is continually evolving, with new platforms and features emerging regularly. Future research should focus on understanding the effects of these new trends and their implications for mental health. Additionally, examining how user behavior changes with new technologies can provide insights into managing potential risks.
Areas for Further Research
Further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of social media use on mental health and to conduct cross-cultural studies to understand how social media impacts individuals in different cultural contexts. Investigating these areas can provide a more comprehensive understanding of social media’s role in mental health and inform strategies for mitigating its negative effects.
Conclusion
Social media has a profound impact on mental health, encompassing both positive and negative aspects. While it offers opportunities for connection, support, and self-expression, it also poses risks such as anxiety, addiction, and sleep disruption. By understanding these effects and implementing strategies to manage social media use, individuals, professionals, and technology companies can work together to promote healthier online experiences and support mental well-being. Continued research and awareness are essential to navigating the complex relationship between social media and mental health in the digital age.
Share This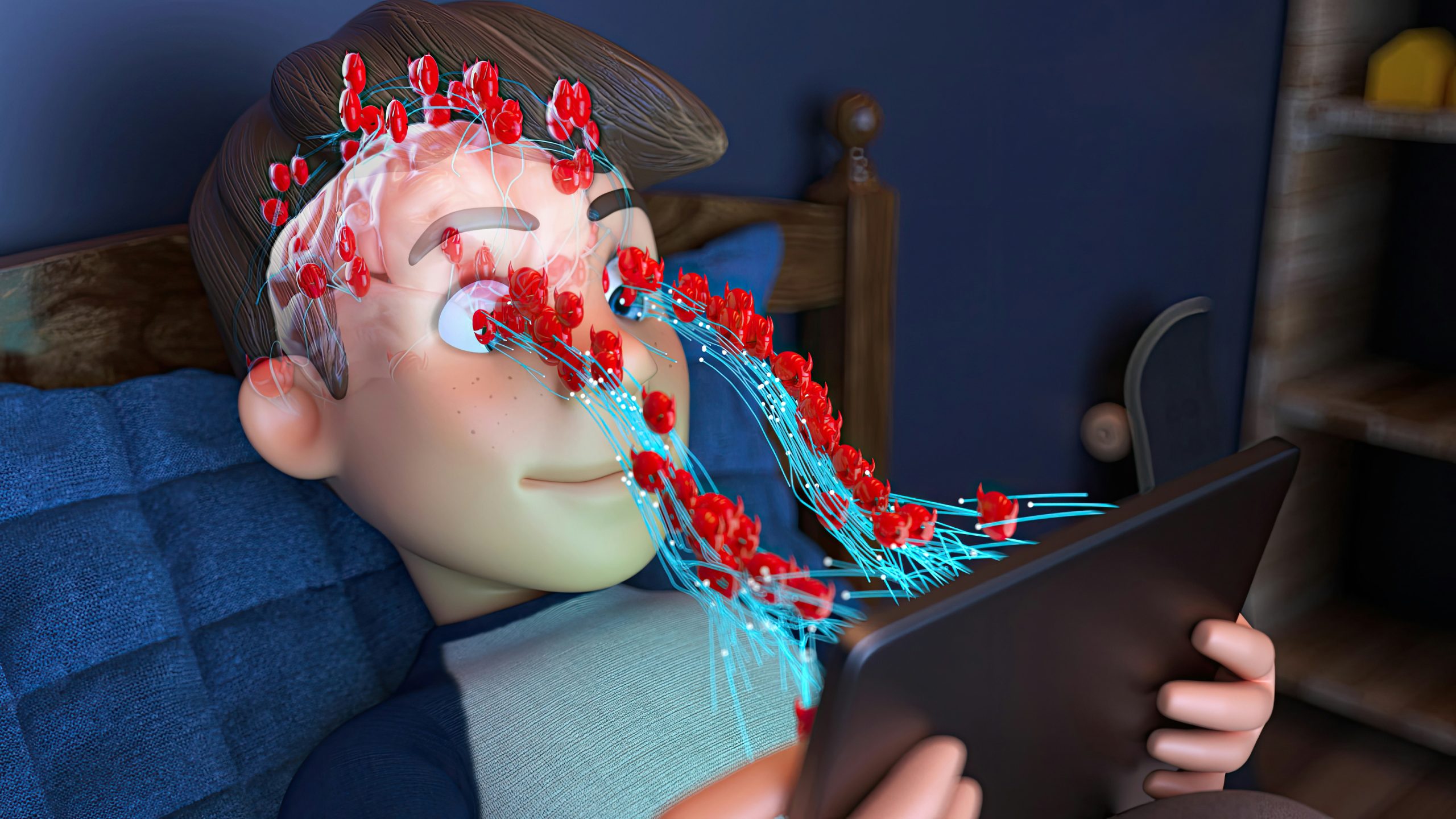




Be the first to comment