Table of Contents
![]()
Social support, a vital aspect of human interaction, encompasses various forms of assistance and resources provided by others. This support can significantly impact individual well-being across different life stages and settings. In this article, we will delve into the types of social support, its significance across life stages, its relationship with health outcomes, its presence in various settings, the challenges associated with it, and strategies to enhance it.
Types of Social Support
Social support can be categorized into four main types: emotional, informational, instrumental, and appraisal support. Each type plays a distinct role in enhancing individual well-being.
- Emotional Support: This type involves providing empathy, care, love, and trust. Emotional support is crucial in alleviating feelings of loneliness and stress. It helps individuals feel understood and valued, which can be particularly beneficial during crises or periods of emotional distress.
- Informational Support: This type includes offering advice, guidance, or information that helps individuals make decisions and solve problems. Informational support is essential for effective decision-making and navigating complex situations, such as managing a health condition or making significant life changes.
- Instrumental Support: This involves providing tangible aid, such as financial assistance, services, or physical help. Instrumental support is vital for addressing immediate needs and practical challenges, such as running errands or providing temporary financial assistance during difficult times.
- Appraisal Support: This type involves providing feedback and evaluations that help individuals assess their situation and performance. Appraisal support can boost self-esteem and confidence by validating experiences and offering constructive feedback.
Social Support Across Different Life Stages
Social support plays a crucial role throughout an individual’s life, impacting various aspects of development and well-being.
- Childhood and Adolescence: During these formative years, family and peer support are pivotal. Positive family interactions and supportive peer relationships contribute to better developmental outcomes, academic success, and emotional resilience. Support from parents and teachers also helps adolescents navigate social challenges and academic pressures.
- Adulthood: In adulthood, social support is vital for career development, job satisfaction, and personal relationships. Support from colleagues, mentors, and friends can enhance job performance and reduce workplace stress. Additionally, strong personal relationships contribute to emotional stability and life satisfaction.
- Aging and Elderly: For older adults, social support is essential for maintaining health and quality of life. Social connections can mitigate feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common in later years. Support from family, friends, and community organizations helps older adults manage health conditions and stay engaged in meaningful activities.
Social Support and Health Outcomes
The impact of social support on health is profound and multifaceted, affecting both physical and mental health.
- Physical Health: Research indicates that social support positively influences immune function and can improve recovery outcomes for chronic illnesses. Individuals with strong social networks tend to have better health behaviors and are more likely to adhere to medical treatments.
- Mental Health: Social support is crucial for mental well-being. It helps reduce the risk of depression, anxiety, and stress by providing emotional comfort and practical assistance. Supportive relationships foster resilience and coping mechanisms, which are essential for managing life’s challenges.
- Behavioral Outcomes: Social support also affects health behaviors. Support from others can encourage positive behaviors such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and avoiding harmful habits. It can also influence adherence to medical advice and treatments.
Social Support in Various Settings
The role of social support extends across different settings, each with its unique dynamics.
- Family: Family members often provide the most immediate and personalized support. The quality of family relationships can significantly impact emotional and practical support. Strong family bonds contribute to overall well-being and resilience.
- Workplace: In the workplace, social support from colleagues and supervisors can enhance job satisfaction and performance. Supportive work environments reduce stress and burnout, fostering a more productive and positive work atmosphere.
- Community: Community support networks, including social groups and organizations, play a crucial role in providing social resources and fostering a sense of belonging. Community engagement can enhance social capital and support individual and collective well-being.
- Online and Digital Support: With the rise of digital communication, online communities and social media platforms offer new avenues for social support. These virtual networks can provide valuable connections and support, although they may also present challenges related to the quality and authenticity of interactions.
Challenges and Barriers to Social Support
Despite its benefits, accessing and providing social support can encounter several challenges.
- Lack of Access to Support: Socioeconomic and geographic factors can limit access to social support. Individuals in isolated or underserved areas may face difficulties in connecting with supportive networks, which can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and reduce overall well-being.
- Quality of Support: Not all support is equally effective. Mismatched support, where the type of assistance provided does not meet the individual’s needs, can be counterproductive. Additionally, excessive dependency on support can sometimes hinder personal growth and self-reliance.
- Cultural and Societal Factors: Cultural norms and values influence how social support is provided and received. Variations in support systems across different cultures can impact the availability and effectiveness of support, highlighting the need for culturally sensitive approaches.
Strategies for Enhancing Social Support
To maximize the benefits of social support, individuals and communities can employ several strategies.
- Building and Maintaining Supportive Relationships: Fostering strong personal connections requires effort and communication. Building trust, practicing empathy, and being present in relationships can enhance the quality of support provided and received.
- Leveraging Community Resources: Identifying and utilizing local and online resources can expand support networks. Engaging with support groups, community organizations, and professional services can provide valuable assistance and connections.
- Developing Support Systems in Various Settings: Improving support structures in workplaces, families, and communities involves creating environments that prioritize and encourage support. Implementing policies and practices that foster supportive interactions can enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
Social support is a fundamental component of human well-being, impacting various aspects of life from mental health to physical health and behavior. Understanding the types of support, its role across different life stages, and its presence in various settings helps highlight its importance. By addressing challenges and employing strategies to enhance support networks, individuals and communities can improve overall quality of life and resilience. Social support, in its many forms, remains a critical factor in navigating life’s complexities and fostering a healthier, more connected society.
Share This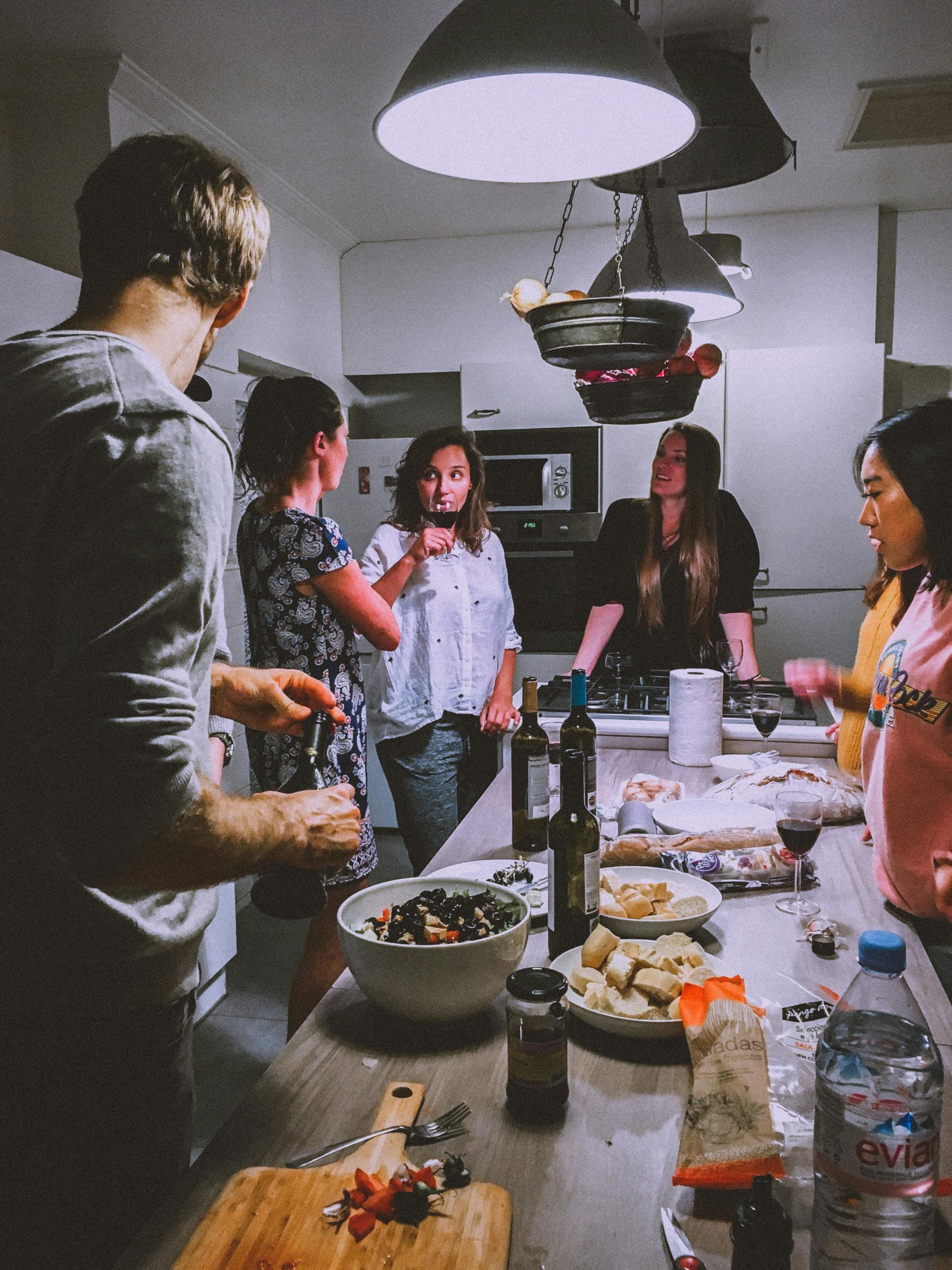



Be the first to comment