Table of Contents
![]()
Introduction
Virtual Reality (VR) therapy is an innovative and rapidly developing field within healthcare that uses immersive virtual environments to treat a wide range of psychological, physical, and cognitive conditions. This technology allows patients to engage with virtual worlds in ways that can aid in therapy, offering an interactive and controlled environment to help with conditions such as anxiety, PTSD, chronic pain, and physical rehabilitation. Over recent years, VR therapy has gained popularity for its potential to revolutionize healthcare practices, offering an alternative or complement to traditional therapeutic methods. This article explores the foundations of VR therapy, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future directions.
Technological Foundations of VR Therapy
Overview of VR Technology
At its core, virtual reality technology consists of hardware and software components that create immersive experiences. The most commonly used VR equipment includes headsets, motion trackers, controllers, and haptic devices that provide sensory feedback. Headsets are designed to display stereoscopic images, allowing users to experience a 3D virtual environment, while motion trackers monitor and respond to a user’s movements, enabling interaction with the virtual world.
Immersive Environments
One of the primary features of VR therapy is the creation of immersive environments. These virtual worlds engage the user’s senses—primarily sight, sound, and touch—by simulating realistic environments and experiences. For example, a patient with a fear of flying may be exposed to a virtual airplane cabin, gradually helping them confront and reduce their anxiety in a safe setting.
Interaction and Feedback
VR therapy is interactive, meaning patients can engage with the virtual environment through their movements and choices. This interaction is critical for reinforcing the therapeutic process. For instance, when undergoing exposure therapy for a phobia, patients might use controllers to interact with objects or characters in the virtual environment, receiving immediate feedback based on their actions, helping to reinforce coping skills or challenge fears.
Software and Platforms
Various software platforms have been developed specifically for therapeutic applications of VR. These platforms simulate environments tailored to specific treatment needs, such as virtual exposure therapy programs for PTSD, anxiety, or phobias. Companies and healthcare providers use these platforms to design VR experiences that allow patients to engage in customized therapeutic sessions.
Applications of VR Therapy
Mental Health Treatment
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): VR therapy has shown promise in treating PTSD by immersing patients in virtual environments that replicate traumatic situations in a controlled, therapeutic context. This form of exposure therapy allows patients to confront and process distressing memories without real-world consequences, often leading to a reduction in PTSD symptoms.
- Anxiety and Phobias: Virtual reality is widely used in treating various anxiety disorders, including social anxiety and specific phobias such as fear of heights or public speaking. By creating virtual scenarios that simulate stressful situations, patients can gradually become desensitized to their triggers in a safe and controlled setting.
- Depression: While more research is needed, VR therapy for depression often involves cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, where virtual environments help patients practice positive thinking, engage in goal-setting, and learn new coping strategies to address negative thought patterns.
- Addiction Therapy: VR therapy is being explored for addiction treatment by simulating situations where patients might experience cravings or temptation. Through these simulations, patients can practice coping strategies and learn to resist urges in a controlled virtual setting.
Pain Management and Rehabilitation
- Chronic Pain: One of the most significant applications of VR therapy is in pain management. By immersing patients in enjoyable and engaging virtual experiences, such as calming nature scenes or interactive games, VR can distract patients from their pain, reducing the perception of discomfort. This technique is particularly effective for chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia or post-surgical pain.
- Physical Rehabilitation: VR-based rehabilitation uses interactive exercises to help patients recover from physical injuries or surgeries. For example, patients recovering from a stroke may use VR to practice motor skills and coordination in a virtual environment, which can help improve their physical function in the real world.
Cognitive Rehabilitation
- Stroke and Brain Injury Recovery: VR therapy is used to support cognitive rehabilitation for patients recovering from strokes or traumatic brain injuries. Virtual exercises can improve memory, attention, motor coordination, and other cognitive functions, helping individuals regain abilities lost due to brain injuries.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders: In patients with conditions like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease, VR therapy is used to provide cognitive stimulation and memory exercises. These virtual experiences help patients stay mentally engaged and may slow the progression of cognitive decline.
Social and Emotional Skills Training
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): VR therapy can provide a safe, non-threatening environment for individuals with autism to practice social interactions and manage sensory overload. For example, a person with ASD may interact with virtual characters in various social situations, learning appropriate responses and communication skills.
- Communication Skills: For individuals recovering from brain injuries or those with developmental disorders, VR simulations offer a controlled space to practice social and communication skills, such as maintaining eye contact or engaging in conversation.
Mechanisms of VR Therapy
Exposure Therapy
A central mechanism in many VR therapies is exposure therapy, where patients confront distressing memories, situations, or fears in a controlled virtual setting. VR exposure therapy allows patients to face their fears without real-world risks, progressively reducing anxiety or trauma-related symptoms.
Immersion and Presence
Immersion, or the sense of “being present” in a virtual environment, plays a critical role in VR therapy. The more immersive the experience, the more effective it can be in promoting emotional engagement and therapeutic change. Studies have shown that VR’s ability to replicate real-world experiences heightens patients’ emotional responses and helps them process difficult emotions.
Distraction and Pain Modulation
For pain management, VR works by distracting patients from their discomfort. By engaging patients in enjoyable or calming virtual experiences, VR diverts attention away from pain signals, effectively reducing the perception of pain. This is particularly useful in medical procedures, rehabilitation, or for chronic pain sufferers.
Behavioral Conditioning
VR therapy also leverages behavioral conditioning techniques, where patients’ actions are reinforced by real-time feedback from the virtual environment. For instance, patients practicing relaxation techniques in a virtual setting may receive positive reinforcement when their physiological responses, such as heart rate or muscle tension, decrease.
Benefits of VR Therapy
Safe and Controlled Environment
One of the primary advantages of VR therapy is its ability to simulate real-world situations in a safe, controlled environment. This is especially valuable for exposure therapy, where patients can gradually confront their fears or trauma without the risk of real-world harm.
Personalization and Customization
VR environments can be tailored to meet the specific needs of individual patients. Whether it’s customizing a virtual exposure therapy scenario or designing rehabilitation exercises, VR therapy allows for a high degree of personalization, improving therapeutic outcomes.
Accessibility and Convenience
VR therapy has the potential to make healthcare more accessible, especially for individuals in remote areas or those with limited mobility. Patients can engage in therapy from the comfort of their home, providing a more convenient and flexible option than traditional in-person sessions.
Engagement and Motivation
The interactive and immersive nature of VR often increases patient engagement and motivation. This is particularly important in rehabilitation or long-term therapy, where maintaining motivation is key to successful outcomes. Gamification elements, such as rewards and progress tracking, can further enhance patient involvement.
Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial investment in VR technology can be high, the long-term costs may be lower than traditional therapy, particularly when considering the potential for remote treatment, reduced hospital visits, and more efficient care delivery.
Challenges and Limitations of VR Therapy
Technical Limitations
The adoption of VR therapy faces several technical barriers. The cost of high-quality VR equipment can be prohibitive for some patients and healthcare providers. Additionally, the need for ongoing maintenance and updates to both hardware and software can pose challenges.
Safety and Side Effects
While VR therapy is generally safe, some users may experience side effects such as dizziness, nausea, or motion sickness, commonly known as VR motion sickness. Additionally, patients with certain psychological conditions, such as severe anxiety or psychosis, may find VR therapy exacerbates their symptoms.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Despite the potential benefits, the high cost and technical complexity of VR equipment may limit its accessibility, particularly for underserved or low-income populations. Furthermore, patients with limited technological literacy may find it difficult to navigate VR platforms.
Lack of Standardized Protocols
There is currently no universal set of guidelines for integrating VR into clinical practice. The lack of standardized protocols makes it difficult for healthcare providers to implement VR therapy consistently across different settings.
Research and Evidence Supporting VR Therapy
Clinical trials and studies have shown that VR therapy can be effective in treating various conditions, including PTSD, anxiety, chronic pain, and rehabilitation. Research from institutions like the University of Southern California and the VA Healthcare System has provided evidence of VR’s efficacy, demonstrating positive outcomes in mental health treatment and physical rehabilitation.
While some studies suggest VR therapy is as effective as traditional treatments, it is often viewed as a complementary tool that can enhance other therapeutic methods, such as CBT or physical therapy.
Future Directions and Innovations in VR Therapy
Advances in VR Technology
The future of VR therapy looks promising, with ongoing advancements in VR hardware making the technology more affordable, portable, and user-friendly. Newer devices, such as standalone headsets, eliminate the need for complex setups, making VR therapy more accessible to patients and healthcare providers.
Integration with AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) could further enhance VR therapy by personalizing treatment plans based on real-time data analysis. AI could track patient progress, adapt VR experiences to meet evolving needs, and provide more targeted interventions.
Expanding Applications
As the field grows, the range of conditions that can benefit from VR therapy will expand. New applications are being explored for conditions such as eating disorders, trauma recovery, and phobias.
Telehealth and Remote Therapy
The rise of telehealth presents an exciting opportunity for VR therapy to be delivered remotely. Patients can engage in therapeutic VR sessions from their homes, making treatment more convenient and accessible.
Global Accessibility
In the future, VR therapy could become a global healthcare solution, offering affordable and accessible mental health and rehabilitation services to underserved populations worldwide.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality therapy holds immense promise in transforming healthcare by providing innovative treatment options for a wide range of psychological, cognitive, and physical conditions. While challenges remain in terms of cost, accessibility, and technical issues, the continued development and adoption of VR technology have the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes. With further research, investment, and refinement, VR therapy could become a mainstream tool in healthcare, helping patients live healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Share This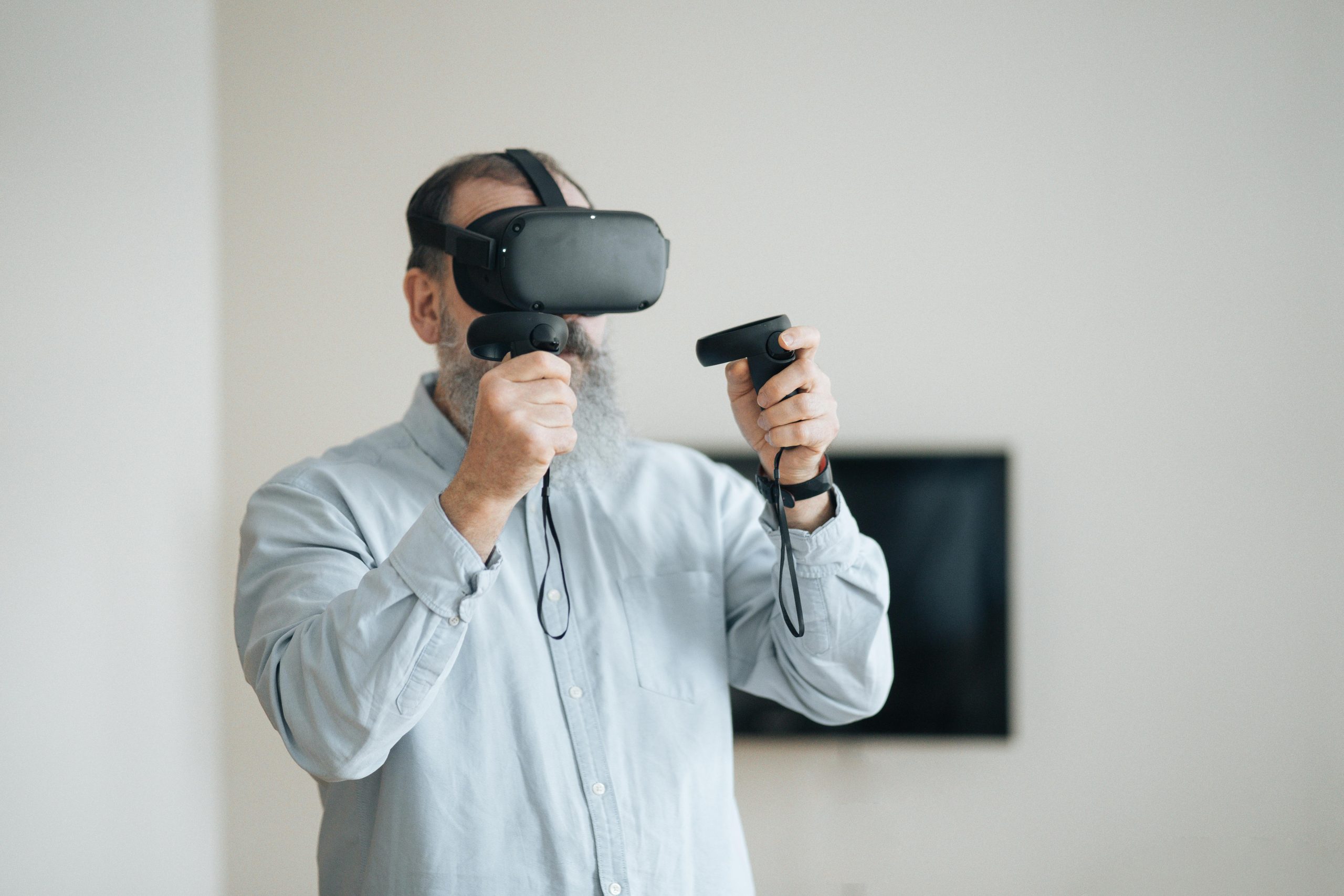




Be the first to comment