Table of Contents
![]()
Introduction
Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that often go unnoticed in the vast expanse of the oceans. However, their role in carbon sequestration, the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, is gaining increasing recognition. In this article, we will delve into the world of algae and explore how these tiny organisms play a vital role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon in the oceans.
Types of Algae
Algae come in a wide array of forms, from microscopic single-celled phytoplankton to large, multicellular seaweeds. While all algae contribute to some extent to carbon sequestration, certain species are particularly relevant due to their high carbon-fixing capabilities. These species are often characterized by their efficient photosynthetic processes.
Mechanisms of Carbon Sequestration
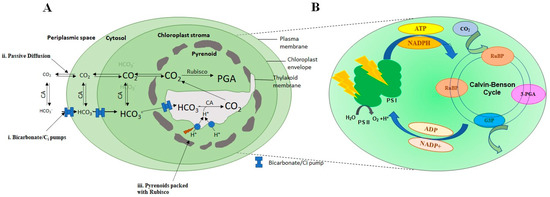
One of the primary mechanisms through which algae sequester carbon is photosynthesis. Just like land-based plants, algae use sunlight to convert CO2 into organic carbon compounds, releasing oxygen in the process. In the ocean, phytoplankton, a type of microalgae, are responsible for a significant portion of carbon fixation. When these tiny organisms photosynthesize, they capture CO2 from the water, effectively removing carbon from the atmosphere.
Factors Influencing Algae’s Carbon Sequestration
Several environmental factors impact the carbon sequestration capacity of algae. Temperature, nutrient availability, and light play critical roles in determining the growth and carbon-fixing potential of algae. Additionally, human activities such as pollution, climate change, and ocean acidification can disrupt the delicate balance of marine ecosystems, affecting algae’s ability to sequester carbon effectively.
Algae and the Carbon Cycle
Algae are integral to the oceanic carbon cycle. They not only capture carbon but also store it in their biomass. When algae die and sink to the ocean floor, they take captured carbon with them, effectively locking it away from the atmosphere for extended periods. This process contributes to the ocean’s role as a massive carbon sink.
Benefits of Algae-Based Carbon Sequestration
The benefits of algae-based carbon sequestration are manifold. First and foremost, it offers a powerful tool for mitigating climate change by reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. Furthermore, algae-based sequestration can improve water quality by removing excess nutrients and promoting the growth of beneficial algae over harmful algal blooms. It also supports biodiversity by providing a habitat for various marine species. Moreover, algae have the potential to yield sustainable products such as biofuels and dietary supplements.
Challenges and Limitations
While algae hold great promise for carbon sequestration, they are not without their challenges and limitations. The occurrence of harmful algal blooms can have detrimental ecological impacts, leading to fish kills and oxygen depletion in aquatic ecosystems. Cultivating algae on a large scale can be technically and economically challenging. Overcoming these hurdles requires innovative solutions and careful management.
Research and Innovations
Researchers worldwide are actively exploring the potential of algae-based carbon sequestration. Innovations range from developing novel cultivation techniques to genetic engineering of algae for enhanced carbon-fixing capabilities. Policy and regulatory developments are also shaping the future of algae-based solutions as governments recognize the importance of this natural carbon capture mechanism.
Future Prospects
As the urgency to combat climate change grows, algae-based carbon sequestration is poised to become a crucial player in mitigating its effects. Scaling up the use of algae for carbon sequestration, integrating it with broader climate change mitigation strategies, and fostering sustainable practices are key steps toward a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Algae, often overlooked in the vast oceans, are emerging as unsung heroes in the battle against climate change. Their remarkable ability to sequester carbon not only helps stabilize our planet’s climate but also offers a range of ecological and economic benefits. It is essential that we recognize the potential of algae-based solutions and invest in research, innovation, and sustainable practices to harness their full potential in addressing one of the most pressing challenges of our time.