Table of Contents
![]()
Introduction
Brown algae, scientifically known as Phaeophyceae, represent a fascinating group of multicellular photosynthetic organisms found primarily in marine environments. Their importance extends beyond ecological significance to encompass various practical applications. In this article, we will delve into the diversity and structure of brown algae, shedding light on their manifold uses.
Diversity of Brown Algae
Brown algae belong to the phylum Ochrophyta and exhibit a remarkable diversity in terms of taxonomy, habitat, and morphology. Taxonomically, they are classified under the class Phaeophyceae, encompassing various orders and families. These organisms inhabit a wide range of aquatic environments, from temperate coastal waters to polar regions and even freshwater habitats. Their morphology varies from filamentous forms to multicellular blades, often characterized by their distinctive brown pigmentation.
Structure of Brown Algae
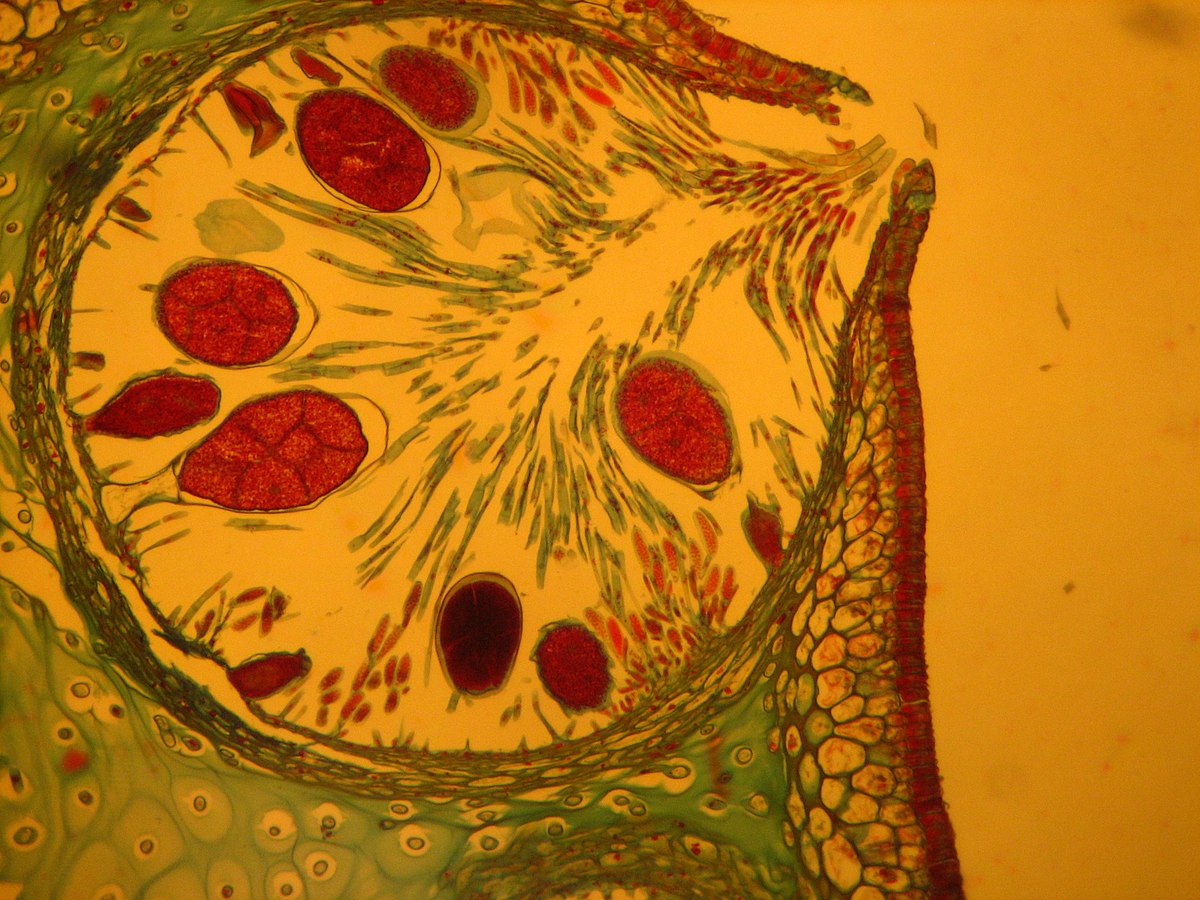
The cellular anatomy of brown algae reveals intriguing adaptations to their underwater habitats. They possess unique cell wall compositions, which include alginates, fucoidans, and cellulose, contributing to their resilience in marine environments. Chloroplasts, equipped with chlorophyll a and c, facilitate photosynthesis, while specialized adaptations like air bladders provide buoyancy. The holdfasts anchor them to substrates, ensuring stability in turbulent waters.
Uses of Brown Algae
- Traditional Uses: Brown algae have long served as a valuable resource for humans. Historically, they have been a food source in many cultures, offering essential nutrients and flavor. Additionally, brown algae are rich sources of alginates, which are extracted and used in various applications. Medicinally, they have been explored for their potential health benefits.
- Industrial Applications: The industrial relevance of brown algae lies in their alginate content. Alginate, derived from these algae, finds application in the food industry as a gelling agent, emulsifier, and stabilizer. In the pharmaceutical sector, alginic acid, another derivative, is utilized in drug formulations. Brown algae extracts are also used in cosmetics and skincare products for their skin-nourishing properties.
- Environmental Importance: Brown algae play a crucial role in the environment. They have been employed in bioremediation efforts to remove heavy metals and pollutants from aquatic ecosystems. Moreover, their capacity to sequester carbon dioxide contributes to mitigating climate change.
- Emerging Uses: As sustainability gains traction, brown algae are being explored for new applications. They hold promise as a feedstock for aquaculture, contributing to sustainable seafood production. Additionally, ongoing research investigates their potential in biofuel production, as they can be a source of renewable energy. Moreover, brown algae are being considered for the development of bioplastics and biocomposites, reducing our reliance on traditional petroleum-based plastics.
Conclusion
Brown algae represent a remarkable group of organisms that thrive in diverse aquatic environments. Their unique diversity and structure have paved the way for numerous applications, from traditional uses in food and medicine to modern industrial and environmental applications. As sustainability becomes increasingly vital, brown algae’s emerging roles in biofuels, aquaculture, and bioplastics underscore their importance in a changing world. Further research in this field promises even more exciting discoveries and applications, highlighting the continued significance of these fascinating organisms.